This task is devoted to multichannel observations of selected well-observed SEP events.
Multi-satellite measurements of solar energetic particles (SEPs) are important both from the point of view of data verification, and for studying the processes of acceleration of particles of different nature.
As an example of such multichannel observations, we present the SEP series, which were observed in the second half of August 2002 (namely from 17 to 25) by two different spacecrafts:
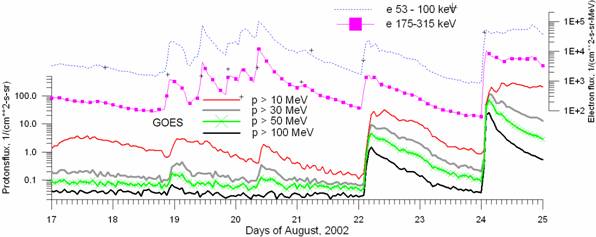
Fig. 1. The evolution of electron fluxes according to the ACE spacecraft data (upper graph) and the integral proton flux according to the GOES spacecraft data integral (lower graph) in the time period 17-25 August 2002.
From Figure 1 it is clearly seen that the ratio of the fluxes of in situ observed electrons and protons is significantly different for the different events. Probably, it is related to different mechanisms of acceleration and escape in the different cases.
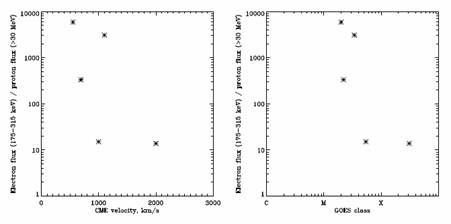
Fig. 2. Scatter plots of electron (ACE) to proton (GOES) ratio vs. CME projected speed (left), vs. GOES flare class (right plot) respectively.
Figure 2 shows the dependences of the ratio of the fluxes of electrons (obtained by ACE) and protons (by GOES) on the speed of the CME and the soft X-ray flare value, respectively. Out of the same flare series observed during August 2002, results for this kind of analysis could be obtained only from five flares. Figure 2 shows a tendency of increasing contribution of solar protons compared to electrons with the increase of, both, the speed of the CME and the GOES flare class (in soft X-rays).
Publications
A.V. Bogomolov, L.K. Kashapova, I.N. Myagkova, Yu. T. Tsap, Dynamics of the x-ray, gamma-ray, and AR 0069 in august 2002 (2014), Astronomy Reports, Vol. 58 (3), pp. 156÷166
A. Bogomolov, I. Myagkova, I. Myshyakov, Ts. Tsvetkov, L. Kashapova, R. Miteva, Comparative analysis of the proton generation efficiency during 17 March 2003 and 11 April 2004 solar flares (2018), JASTP, Vol. 179, pp. 517÷526